The Crozier Fire, a significant wildfire in the Sierra Nevada, serves as a stark reminder of the increasing risks and devastating impacts of wildfires. This article provides an in-depth analysis of the Crozier Fire, examining its causes, progression, and the challenges faced by firefighters. It also explores the human and environmental consequences and, most importantly, extracts crucial lessons for enhancing community resilience and preventing future wildfire disasters.
Decoding the Crozier Fire: A Chronicle of a Wildfire
Wildfires have become an ever-present threat to communities in fire-prone regions. The Crozier Fire’s swift spread and destructive power underscore the urgent need for comprehensive wildfire management strategies. This article aims to dissect the Crozier Fire, offering a detailed account of its timeline, the factors contributing to its intensity, and the efforts undertaken to contain it.
Genesis of the Inferno: The Crozier Fire’s Ignition and Early Spread
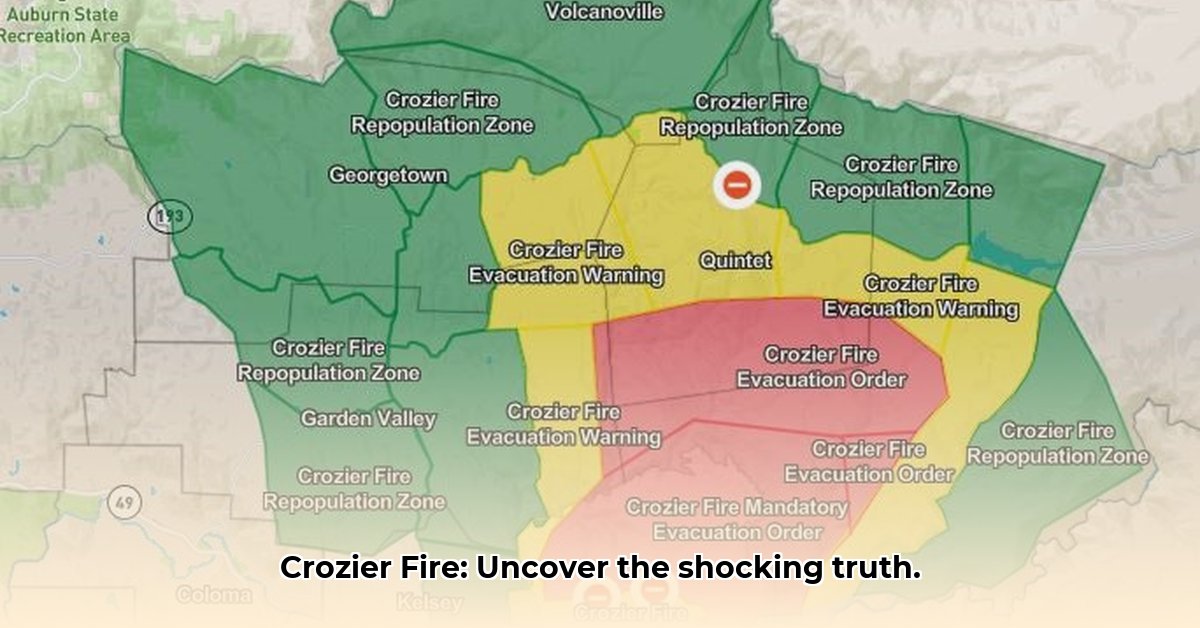
The Crozier Fire was reported on August 6, 2024, as a half-acre vegetation fire in the Eldorado National Forest, approximately six miles north of Camino. Fueled by dry vegetation and aided by gusty winds, the fire quickly escalated, prompting immediate evacuations of nearby communities.
Anatomy of a Wildfire: Factors Fueling the Crozier Fire’s Growth
Several factors contributed to the rapid growth and intensity of the Crozier Fire:
- Abundant Dry Fuel: The Sierra Nevada region was experiencing prolonged drought conditions, leading to an abundance of dry vegetation that readily ignited and fueled the fire.
- Steep Terrain: The rugged and steep terrain of the Eldorado National Forest made it difficult for firefighters to access the fire and establish effective containment lines.
- Erratic Winds: Shifting winds pushed the fire in unpredictable directions, making it challenging to anticipate its spread and deploy resources effectively.
Battling the Blaze: Fire Suppression Strategies and Challenges
Firefighters employed a variety of strategies to combat the Crozier Fire, including:
- Air Support: Air tankers dropped fire retardant to slow the fire’s spread and protect structures.
- Ground Crews: Ground crews worked to establish containment lines by clearing vegetation and creating firebreaks.
- Dozer Operations: Dozers were used to improve secondary and tertiary contingency lines, serving as fuel breaks in future fire events.
Despite these efforts, firefighters faced significant challenges, including the fire’s rapid spread, difficult terrain, and erratic winds.
Impact Zone: Evacuations, Losses, and Community Disruption
The Crozier Fire forced the evacuation of numerous communities in the Sierra Nevada, including Volcanoville, Quintette, Spanish Flat, and part of Georgetown. The fire damaged or destroyed homes and businesses, causing significant economic disruption. The smoke generated by the fire also impacted air quality in the region, posing health risks to residents. El Dorado County established a non-emergency line at (530) 621-7676 for fire information.
Data Analysis: Reconciling Discrepancies in Fire Size Reports
Official reports on the Crozier Fire’s size varied, likely due to the challenges of tracking a dynamic fire in real-time. These inconsistencies underscored the need for improved data collection and reporting methods, including the use of advanced technologies such as drones and satellite imagery.
Lessons from the Ashes: Wildfire Mitigation and Prevention Strategies
The Crozier Fire provides valuable lessons for mitigating future wildfire risks:
- Fuel Management: Proactive forest management practices, such as thinning and prescribed burns, can reduce the amount of fuel available to wildfires.
- Early Detection and Rapid Response: Investing in early detection systems and ensuring a swift and coordinated response can help contain wildfires before they escalate.
- Community Preparedness: Educating residents about wildfire risks and providing them with resources to prepare their homes and communities can significantly reduce losses.
- Infrastructure Hardening: Retrofitting homes and businesses with fire-resistant materials and maintaining defensible space around structures can improve their chances of survival.
Building Resilience: Community-Based Wildfire Protection Plans
Community Wildfire Protection Plans (CWPPs) are collaborative efforts that bring together residents, local governments, and fire agencies to identify and address wildfire risks at the community level. CWPPs can include strategies for fuel management, structure protection, evacuation planning, and community education.
Future-Proofing: A Proactive Approach to Wildfire Management
The Crozier Fire underscores the need for a proactive and comprehensive approach to wildfire management. By investing in prevention, preparedness, and response efforts, communities can reduce their vulnerability to wildfires and build a more resilient future.
A Call to Action: Protecting Communities from Future Wildfires
The Crozier Fire serves as a wake-up call, urging communities to take action to protect themselves from the growing threat of wildfires. By implementing the lessons learned from the Crozier Fire and adopting a proactive approach to wildfire management, we can build a safer and more resilient future for all.
Optimizing Wildfire Resource Allocation: Insights from the Crozier Fire
Key Takeaways:
- The Crozier Fire highlighted deficiencies in resource allocation strategies.
- Data-driven improvements in predictive modeling are essential.
- Strong communication and collaboration are critical for successful wildfire responses.
- Technological investments, particularly in GIS systems, are paramount.
- Community involvement is crucial for minimizing potential losses.
The Crozier Fire: A Case Study in Resource Allocation
The Crozier Fire underscores the critical need for optimized resource allocation in wildfire management. Analyzing the fire’s spread and suppression efforts offers invaluable insights for improving future responses. The Crozier Fire is a case study of what can happen when resources are not optimally allocated.
Analyzing Fire Behavior: Understanding the Drivers
Fuel load, terrain characteristics, and prevailing weather patterns significantly influenced the Crozier Fire’s quick spread. Understanding these factors is essential for developing accurate predictive models. Terrain is a major factor in how a fire spreads.
Evaluating Suppression Effectiveness: Strategies and Resources
The suppression efforts deployed during the Crozier Fire included air tankers, ground crews, and heavy equipment. Evaluating the effectiveness of these resources is essential for identifying areas for improvement. Were resources deployed at the right time and in the right place?
Data Integrity: Transparency and Accuracy in Reporting
Discrepancies in official reports regarding the Crozier Fire’s size highlight the need for enhanced data collection and reporting protocols. Transparent and accurate data is critical for effective decision-making.
Quantifying Impact: Economic and Social Costs
The Crozier Fire resulted in significant economic losses and widespread evacuations, underscoring the importance of proactive prevention measures. The financial and emotional toll of wildfires can be devastating to individuals and communities.
Lessons Learned: Preparedness and Emergency Response
The Crozier Fire reinforces the importance of community wildfire preparedness and improved interagency communication. These are critical components of an effective emergency response. Have communities developed comprehensive evacuation plans?
Long-Term Implications: Ecological Recovery and Community Resilience
Addressing the long-term ecological impacts of the Crozier Fire and fostering community resilience are essential for sustainable recovery. This includes strengthening social networks and providing support services. What steps are being taken to restore the affected ecosystems?
Actionable Recommendations: Enhancing Wildfire Management
- Improve Predictive Modeling: Implement advanced GIS data and modeling techniques for more accurate wildfire predictions.
- Optimize Resource Allocation: Develop algorithms that use real-time fire behavior analysis to efficiently allocate resources.
- Enhance Communication and Coordination: Establish clear and consistent communication protocols among agencies and stakeholders.
- Invest in Technology: Upgrade equipment and communication systems, including GIS maps and real-time data feeds.
- Strengthen Community Resilience: Actively engage communities in developing and implementing preparedness plans.
Crozier Fire Suppression: Terrain Challenges in the Sierra Nevada
Key Takeaways:
- Rapid containment demonstrated the effectiveness of coordinated firefighting efforts.
- The substantial cost ($28,755,389) underscores the financial burden of wildfire management.
- The challenging Sierra Nevada terrain presented unique suppression obstacles.
- Long-term ecological consequences necessitate ongoing monitoring and restoration efforts.
- Uncertainty surrounding the fire’s cause highlights the need for enhanced prevention strategies.
Terrain as a Factor: Understanding the Sierra Nevada’s Impact
The Sierra Nevada’s steep slopes, dense vegetation, and variable weather patterns significantly complicated suppression efforts during the Crozier Fire. Terrain limitations affected access for ground crews, and dry fuels acted as ready kindling.
Resource Deployment and Strategic Approaches
Combating the Crozier Fire required a combination of air tankers and ground crews. The overarching strategy focused on containing the fire’s perimeter to prevent its encroachment into populated areas. A total of 1,001 personnel were ultimately involved in the suppression efforts.
Analyzing Containment: Addressing Data Discrepancies
Although the Crozier Fire’s containment progressed relatively quickly, discrepancies in reported data highlight the challenges of maintaining accuracy in dynamic situations. Accurate, real-time data is crucial for effective incident command decisions.
Economic and Social Burdens
The Crozier Fire’s cost of $28,755,389 underscores the significant economic burden of wildfire suppression. Evacuations caused considerable stress and disruption, and smoke impacted public health.
Lessons Learned: Implications Moving Forward
The Crozier Fire emphasizes the need for improved predictive models and refined suppression strategies. Prevention and community engagement are also crucial components of any comprehensive wildfire management plan. The ecological impact, including soil erosion and habitat loss, must also be addressed.
Recommendations for Improved Wildfire Management
- Invest in Advanced Technology: Enhance early warning systems specifically
- Why Do My Installation Keep Stopping on Xbox? - February 16, 2026
- How to Fix Installation Stopped Xbox One Digital Download - February 15, 2026
- Resolve Game Not Installing on Xbox One Installation Problems - February 14, 2026